
mkdir - Create a new directory
mkdir new_directory namemkdir new_direactory name or folder name
mkdir Shivarajughm
mkdir -vp Shivarajughm
m --> Sets the access mode for the new directory.
-p--> If the parent directories don't exist, this command creates them.
-v--> Print a message for each created directory
mkdir -vp Shivarajughm/Linux/ShellScript/Git/Maven/Tomacat/SonarQube
The touch command creates an empty file with zero bytes.
touch devops.txt
touch file1 file2 shiva.txt
cd - Change directory
cd Shivarajghm
To come out of a present directory
cd - it will take a working directory
cd -
If you want to go home directory
cd ~
If you want to go 3 levels up
cd ../../..
If you want to come out of 2 or more directories.
cd ../../
To move to the absolute path.
cd /shivarajughm1/shivarajughm2/
cd /home/user/
PWD - Print the current working directory
pwd
vi :- it is the create file & update the file.
it is going open in the command mode press the i --> it will comes insert mode.
press esc I – insert mode in vi editor.
after that, we enter the details. then we have to the save file.
Press esc: wq! – save and quit the file. W-write,q-quit,!-forcefully.
Press esc: q! – quit without saving the content.
Press esc: set number or se nu – which sets the number for a file.
vi devops.txt
Hi hello
how are you
Awk command :- it Is used to cut the content of a file column-wise.
you can see this is also the same all the content in the file I want to print that particular only first color $0,$1,$N these are field variables.
vi ghmfamily.txt
cat ghmfamily.txt
=============================================================
FirstName LastName SurName Occupation Place
=============================================================
Mahanandi Swamy GHM Business Gulyam
Sreedevi --- GHM House Wife NDM
Shivaraju Swamy GHM DevOps engi Bangalore
Divya Swamy GHM D.e.O Ballari
basava Swamy HM G.R.B Ballari
Pooja swamy GHM student Ballari
==================================================================
awk '{print $(NF)}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $(NF-1)}' ghmfamily.txt
awk ‘{print $2,$3}’ filename -2nd and 3rd col
Ls –lrt | awk ‘{print $NF}’ –last col
Ls –lrt | awk ‘{print $2,$3}’
Ls –lrt | awk ‘{print $(NF-1)}’ -2nd last col
awk '{print}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $0}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $1}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $2}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $3}' ghmfamily.txt
awk '{print $1,$2,$5}' ghmfamily.txt
ls --> Lists the contents of your current working directory.
Some options with ls are :
-l --> list in long format
-a--> all files including those which begin with dot
-F--> It is used to classify the directories and executables. It will append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
-i --> list the inode number in the first column
-R--> recursively list all directories and subdirectories
-r--> Display in reverse order.
-t--> sorts files by access time.
Files start with : ( – )
Directories start with : ( d )
Links start with : ( l )
list files and directories with long ( It will show in alphabetical)
ls –lLong list format with time
ls –ltit will display reverse-order files and directories.
ls –lrtit will display a list of the hidden files
ls -arm - Remove a file or directory:
rm file.txt or rm -r directory
rmdir --> This command is used to remove the directory.
rmdir directoryname
it is going to all directories & all files in the current directory
rm -rf *
cp - Copy a file or directory:
cp file.txt /home/user/ or cp -r directory /home/user/
mv - Move or rename a file or directory:
mv file.txt /home/user/ or mv oldname.txt newname.txt
cat - used to display the content of a file on the console.
cat shivarajughm.txt
less - Display the contents of a file one page at a time
less file.txt
tail - Display the last few lines of a file
tail filename.txt or tail file1 file2 file3
head - Display the first few lines of a file:
head file.txt or head file1 file2 file3
Grep: Is used to search pattern/string in a file without opening the file/console
grep 'pattern' file.txt
Grep “pattern” filename
Grep –w “pattern” filename It is used to search only word
It will give the pattern present in all the files.
Grep pattern *
prints only file names whose pattern is present
Grep –l “pattern” *
Grep –R –l “pattern” * or rgrep “pattern” file
used to count number of lines. Give the count of the pattern in the files.
Grep –c “pattern” *
used to search multiple patterns Also u can use egrep “pattern1” , “pattern2”
Grep –e “pattern1” –e “pattern2” * or egrep "pattern1","pattern2"
used to print all lines starting with w from the given file
Grep ^w filename
used to print all lines which end with pattern e from the given
Grep e$ filename
Pipe filters (|):- Pipe is used to give an output of one command as the input to the next command.
ls –lrt > log.txt | cat log.txt
FIND: using the find command we can search the file search directories with various conditions.
How to find the empty files in the current directory, find. (dot) represent in the Linux
find . -type f -empty
how to find home directory
find ~ -type f -empty
if you want to search the entire file system uses the root directory
find / -type f -empty
tar - Create or extract a tar archive
tar -cvf archive.tar file.txt or tar -xvf archive.tar
gzip - Compress or decompress a file
gzip file.txt or gzip -d file.txt.gz
curl - Transfer data from or to a server
curl https://example.com/
wget - Download a file from the web
wget https://example.com/file.txt
Ping:- Is used to check whether the server is up or down.
Ping - Test network connectivity
Ping ip or ping hostname
traceroute - Trace the path taken by packets over the network:
traceroute example.com
ssh - Connect to a remote server securely
ssh - it is used to connect to a remote server.
ssh user@example.com
ssh user-name@host-name/IP(servername)
scp - Copy files securely between hosts or it Is used to copy files or dir from one server to another server.
Scp file username@server2:/home/dir1/dir2/
Password: abc@123#**
Scp –r dir1 username@server2:/home/../../
Scp –p file1 username@server2:/home/../../
P is preserved permission as same
scp file.txt user@example.com:/home/user/
Rsync:- it is used to copy files from one server to another server and also within the server, while copying the data if a copy is stopped due to network issues in between, if I use ‘scp’ it will start copying from begin if I use rsync it will start copying from where it is stopped.
rsync :- Synchronize files and directories between hosts
rsync file username@server2:/home/test/../
rsync -avz file.txt user@example.com:/home/user/
rsync src dest
TOP:- Display system processes and their resource usage
The top utility is a commonly used tool for displaying system-performance information. It dynamically shows administrators which processes are consuming processor and memory resources.
ps - Display information about running processes:
ps -ef | grep service name
kill - Send a signal to a process to terminate it
kill process id
netstat - Display network connections and their status:
netstat -an
ifconfig - Display network interface configuration:
ifconfig
route - Display or modify the kernel's routing table:
route -n
iptables - Configure firewall rules:
iptables -l
hostname - Display or set the hostname of the system:
hostname or hostname new_hostname
hostname -i
name - Display system information:
uname -a
uname -v
free - Display memory usage:
free -m
free -h
free -g
free -k
df - Display disk space usage:
df -h
du - Display disk usage by directory:
du -sh /home/user/
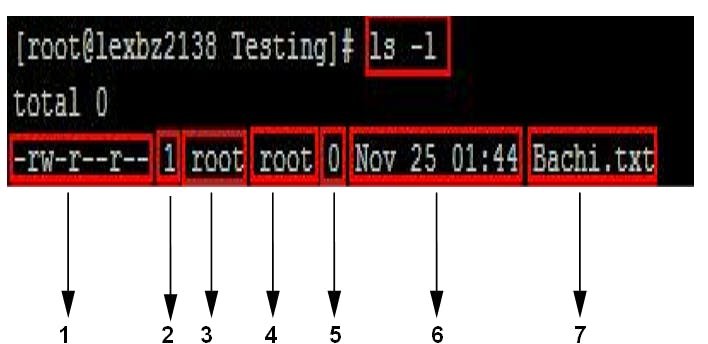
1) Permissions
2) Number of links
3) Owner
4) Group Owner
5) Size of the File in Bytes
6) Date and Time of created
7) File name/Dir Name
Access Permissions Chmod command
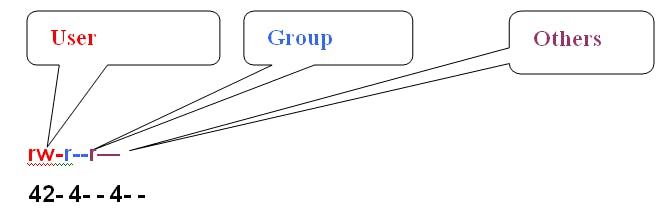
Used to change permission of a file or directory
-r-- r-- r-- :- file or directory or link,
rwx=user, r--=group, r--=others R=read,w=write,x=execute
It will be in binary format r=4. w=2. x=1
umask -->user mask is used to set the permission for files/directories.
| umask value | directory value | file value | |
| root user value is | 0022 | 755 | 644 |
| normal user value is | 0002 | 775 | 664 |
| Base permissions for dir are | 0777 |
| (-) 0222 | |
| 0755 |
once created with directory 755 permissions
same way default file permissions set
| Base permissions for files are | 0666 |
| (-) 0222 | |
| 0644 |
r --> read -->4
w --> write-->2
x--> execute-->1
we are getting 775 permissions
421 421 4-1
rwx rwx r-x
Chmod 777 filename – all permission to a file
Chmod u+w file –user and write permission to a file Group and other full permission 277
chmod u+w file 277
Chmod g+rwx,o+rwx file 077 (+ Adding the permission)
Chmod g-w,o-w file 722 (- Removing the permission)
Chmod a+rwx file 777
chmod 644 file.txt or chmod -R 755 directory/
chown - Change the owner of a file or directory
chown user file.txt or chown -R user directory/